Persistent Storage with OpenEBS
Posted on by Josh Kasuboski · 3min read
My cluster monitoring prometheus kept falling over because it was running out of disk space. After finally getting annoyed having to restart it, I decided it was time for persistent storage.
I did have the local-path-provisioner running, but I didn’t feel great about using the SD card for general storage.
I bought 2 USB drives to add to my workers. In hindsight, I probably should have gotten 3 for better redundancy.
I decided to go with OpenEBS. It works as Container Attached Storage and seemed more lightweight and flexible than other options. They also publish arm64 images which is always a plus.
Prepare the cluster
I found the OpenEBS docs a little hard to follow, but this is what I ended up doing.
- Attach your USB drives to the workers (hopefully yours are labeled)
- install iscsi on every node
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y open-iscsi
sudo systemctl enable --now iscsid
Install OpenEBS
I installed using the helm chart. The only changes with the values file below is basically changing all images to the arm64 version. It seems they don’t have great support for a mixed architecture cluster.
kubectl create ns openebs
helm repo add openebs https://openebs.github.io/charts
helm install openebs openebs/openebs --namespace openebs --version 1.11.1 -f openebs-values.yaml
ndm:
image: 'openebs/node-disk-manager-arm64'
ndmOperator:
image: 'openebs/node-disk-operator-arm64'
webhook:
image: 'openebs/admission-server-arm64'
apiserver:
image: 'openebs/m-apiserver-arm64'
localprovisioner:
image: 'openebs/provisioner-localpv-arm64'
snapshotOperator:
controller:
image: 'openebs/snapshot-controller-arm64'
provisioner:
image: 'openebs/snapshot-provisioner-arm64'
provisioner:
image: 'openebs/openebs-k8s-provisioner-arm64'
helper:
image: 'openebs/linux-utils-arm64'
cstor:
pool:
image: 'openebs/cstor-pool-arm64'
poolMgmt:
image: 'openebs/cstor-pool-mgmt-arm64'
target:
image: 'openebs/cstor-istgt-arm64'
volumeMgmt:
image: 'openebs/cstor-volume-mgmt-arm64'
policies:
monitoring:
image: 'openebs/m-exporter-arm64'
analytics:
enabled: false
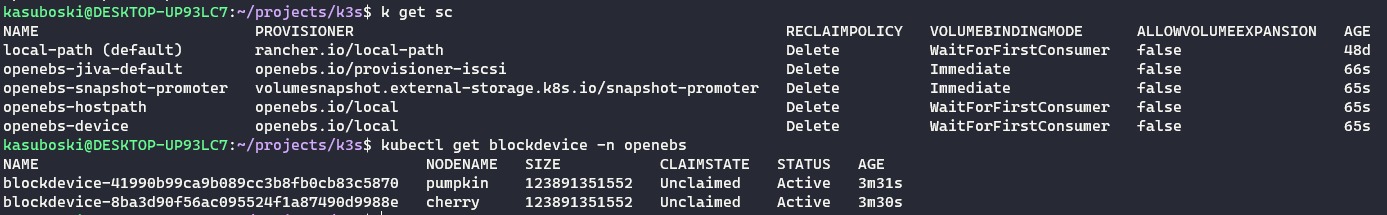
If all is well you should see the pods in the openebs namespace as healthy. My usb drives automatically showed up as block devices as well.
kubectl get pods -n openebskubectl get sckubectl get blockdevice -n openebs
Configure OpenEBS
I differed from the quickstart a little bit here. It was a little confusing to me what I should do with only 2 devices.
I eventually found this issue talking about configuring volumes with a single replica and made it use 2 pools instead of 1.
The below yaml will set up a StoragePoolClaim with a maxPools of 2 (which will just use both of my nodes with a drive) and a StorageClass configured to use a single replica. I went with striped because it seemed more flexible and since each node only has 1 disk right now it didn’t seem too important.
---
apiVersion: openebs.io/v1alpha1
kind: StoragePoolClaim
metadata:
name: cstor-disk
spec:
name: cstor-disk
type: disk
maxPools: 2
poolSpec:
poolType: striped
---
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: openebs-cstor-1-replica-disk
annotations:
openebs.io/cas-type: cstor
cas.openebs.io/config: |
- name: StoragePoolClaim
value: "cstor-disk"
- name: ReplicaCount
value: "1"
provisioner: openebs.io/provisioner-iscsi
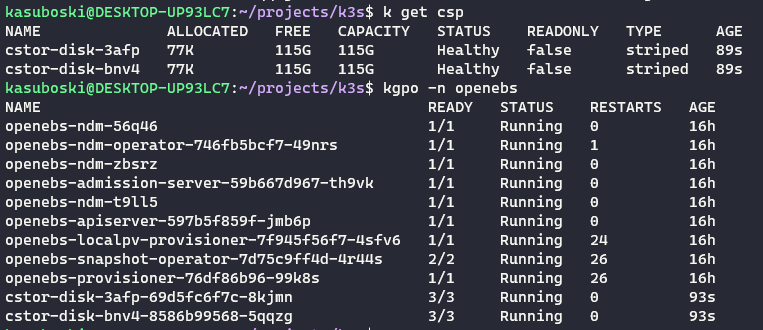
After this is applied, you should be able to see the claims and corresponding pods.
Persistent Prometheus
I used this StorageClass for my cluster Prometheus. It took awhile for the PersistentVolumeClaim pod to start so the initial mount timed out. After around 5 minutes, it sorted itself out. I was able to delete the Prometheus pod and still retained data.